"सैंटियागो": अवतरणों में अंतर
नया पृष्ठ: {{अनुवाद}} '''सेंटियागो''' चिली देश की राजधानी है। यह देश के केन्द्री... |
(कोई अंतर नहीं)
|
15:05, 30 अप्रैल 2008 का अवतरण
| यह सम्पूर्ण पृष्ठ या इसके कुछ अनुभाग हिन्दी के अतिरिक्त अन्य भाषा(ओं) में भी लिखे गए हैं। आप इनका करके विकिपीडिया की सहायता कर सकते हैं। |
सेंटियागो चिली देश की राजधानी है। यह देश के केन्द्रीय घाटी में समुद्र तल से लगभग ५२० मी की उंचाई पर स्थित है। लगभग दो दशकों की निर्बाध आर्थिक प्रगति ने लातिनी अमरीका में सेंटियागो को सबसे आधुनिक शहरों में शुमार कर दिया है और आज यहां दर्जनों शॉपिंग मॉल एवं सैकडो़ उंची इमारते हैं।
इतिहास
सेंटियागो की स्थापना एक स्पैनिश नागरिक पेद्रो दे वाल्दिविया द्वारा२१ फरवरी, १५४१ मे की गयी थी। स्थापना समारोह ह्यूलेन हॉल में की गयी थी जिसे बाद में सेरो सांता लूसिया नाम दिया गया। श्री वाल्दिविया ने इस जगह का चुनाव इस जगह की अच्छी जलवायु एवं परिवहन के लिए आसानी से उपलब्ध मापोचो नदी की वजह से की थी। १ सितंबर १५४१ को अराको युद्ध में यह शहर पूरी तरह तहस नहस हो गयी थी।

The first buildings were erected with the help of the native Picunche Indians. The south bank of the Mapocho River was later drained and converted into a public promenade, known as the Alameda (now Avenida Alameda Libertador Bernardo O'Higgins). The city was slightly damaged during the War of Independence (1810–18), in the Battle of Maipú, which was fought south-west of the city. Santiago was named capital in 1818.

During the early 19th century, Santiago remained a small town with few buildings excepting Palacio de La Moneda, the building used as the Chilean mint during the Spanish period, and a few churches and other civic buildings. The Iglesia de la Compañía de Jesús caught fire during an 1863 church service, and 2000 people died, one of the worst modern fires.[1]
In the 1880s extraction of nitrate fertilizer in Northern Chile brought prosperity to the country, and promoted the capital city's development. Important landmarks were built in 1910 during the Centennial celebrations of independence from Spain, such as the National Library, the Museum of Fine Arts and the Mapocho Train Station (Estación Mapocho, now an events center).
Santiago began its transformation into a modern city in the 1930s, with the building of the Barrio Cívico, surrounding Palacio de La Moneda. The city also grew in population, due to migration from the north and south of Chile. In 1985 an earthquake destroyed some historically significant buildings in the downtown area.
Nowadays, Santiago is among the largest and most important financial centers in Latin America.[तथ्य वांछित]
भूगोल

The city lies in the center of the Santiago Basin, a large bowl-shaped valley consisting of a broad and fertile plain surrounded by mountains. It is flanked by the main chain of the Andes on the east and the Chilean Coastal Range on the west. On the north, it is bound by the Cordón de Chacabuco, a transverse mountain range of the Andes, whereas at the southern border lies Angostura de Paine, where an elongated spur of the Andes almost reaches the Coastal Range. Santiago Basin is part of the Intermediate Depression and is remarkably flat, interrupted only by a few hills. Among those are Cerro Renca, Cerro Blanco and Cerro Santa Lucía.
The Andes mountains around Santiago are quite tall, culminating in Tupungato volcano at 6,570 मी॰ (21,555 फीट). Other volcanoes include Tupungatito, San José and Maipo. Cerro El Plomo is the highest mountain visible from Santiago's urban area.
जलवायु

Santiago has a mild Mediterranean climate: relatively hot dry summers (November to March) with temperatures reaching up to 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit) on the hottest days; winters (June to August) are more humid and cold mornings, with typical maximum daily temperatures of 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit), and minimums of a few degrees above freezing. Occasional snowfall occurs on the suburbs that are highest, and may extend to the rest, but infrequently (the last snowfall reaching down to the city center was in August 2007). Mean rainfall is 358 mm per year.
| महीने | जनवरी | फ़रवरी | मार्च | अप्रैल | मई | जून | जुलाई | अगस्त | सितम्बर | अक्टूबर | नवम्बर | दिसम्बर | वर्ष |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| उच्चमान°C (°F) | 37 (99) |
36 (97) |
34 (93) |
31 (88) |
25 (77) |
23 (73) |
19 (66) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
30 (86) |
33 (91) |
37 (99) |
37 (99) |
| औसत उच्च°C (°F) | 29 (84) |
28 (82) |
26 (79) |
19 (66) |
14 (57) |
13 (55) |
12 (54) |
13 (55) |
15 (59) |
20 (68) |
25 (77) |
27 (81) |
19 (66) |
| औसत निम्न °C (°F) | 15 (59) |
14 (57) |
10 (50) |
7 (45) |
5 (41) |
3 (37) |
2 (36) |
3 (37) |
5 (41) |
7 (45) |
10 (50) |
15 (59) |
8 (46) |
| निम्नमान °C (°F) | 6 (43) |
5 (41) |
4 (39) |
-2 (28) |
-3 (27) |
-6 (21) |
-7 (19) |
-7 (19) |
-5 (23) |
-2 (28) |
2 (36) |
7 (45) |
−7 (19) |
| वर्षा mm (इंच) | 0.4 (0.02) |
0.8 (0.03) |
3.2 (0.13) |
20.4 (0.8) |
52.2 (2.06) |
70.4 (2.77) |
86.6 (3.41) |
61.8 (2.43) |
32.0 (1.26) |
13.4 (0.53) |
9.2 (0.36) |
5.1 (0.2) |
355.5 (14) |
| स्रोत: January 5, 2008 | |||||||||||||
पारिस्थतिक मुद्दे
Thermal inversion (a meteorological phenomenon whereby a stable layer of warm air holds down colder air close to the ground) causes high levels of smog and air pollution to be trapped and concentrate within the Central Valley during winter months. In the 1990s air pollution fell by about one-third, but there has been little progress since 2000.
As of March 2007, only 61% of the wastewater in Santiago was treated [2], which increased up to 71% by the end of the same year, however, the Mapocho river, which crosses the city from the north-east to the south-west of the Central Valley, remains contaminated by household, agricultural and industrial sewage, and by upstream copper-mining waste (there are a number of copper mines in the Andes east of Santiago), being dumped unfiltered into the river.[3] Laws force industry and local governments to process all their wastewater, but are loosely enforced.[4] There are now a number of large wastewater processing and recycling plants under construction. There are ongoing plans to decontaminate the river[5] and make it navigable[6].
Noise levels on the main streets are high [7], mostly because of noisy diesel buses. Diesel trucks and buses are also major contributors to winter smog. A lengthy replacement process of the bus system began in 2005 and will last until 2010 (see Transportation section below).
जनसांख्यिकी


The population of Santiago's urban agglomeration grew from 0.982 million in 1940 to 2.82 million in 1970 and 4.75 million in 1992. According to the 2002 census, it contains a population of about 5.47 million, equivalent to nearly 37% of the total population of the country and 43% of the total urban population, making it one of the largest cities in Latin America. Santiago's Metropolitan Area, according to an official estimate from 2006, has a population of 6.293 million people.
The city is increasingly receiving immigration from other countries in Latin America due to comparatively strong economic growth. Many Peruvians live in Santiago, as well as Bolivians, Argentines, and Ecuadorians.
अर्थव्यवस्था

Santiago is the industrial and financial center of Chile, and generates 45 percent of the country's GDP. [तथ्य वांछित] The city, along with Buenos Aires and São Paulo, is one of the main financial centres of South America. Some international institutions, such as ECLAC (Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean), have their offices in Santiago.
In recent years, due to the strong growth and stability of the Chilean economy [तथ्य वांछित], many multinational companies have chosen Santiago as the place for their headquarters in the region, like HP, Reuters, JP Morgan, Intel, Coca-Cola, Unilever, Nestlé, Kodak, BHP Billiton, IBM, Motorola, Microsoft, Ford, Yahoo!, and many more.
निर्माण
The construction sector is booming in Santiago. [तथ्य वांछित] Several large apartment complexes are being built throughout the city and construction cranes are a common sight. Currently under construction is the Costanera Center, a mega project in Santiago's Financial District. This includes a 280,000-वर्ग-मीटर (3,014,000 वर्ग फुट) mall, a 300-मीटर (980 फीट)* tower, two office towers of 170 मीटर (558 फीट)* each, and a hotel 105 मीटर (344 फीट)* tall. When completed in 2010 it will be the tallest building in South America. Near Costanera Center another skyscraper is being built, Titanium La Portada, and this will be 190 मीटर (623 फीट)* tall. Although these are the two biggest projects, there are many other office buildings under construction in Santiago, as well as hundreds of high rise residential buildings.
यातायात
वायु

Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport is Santiago's national and international airport.
रेल

Trains operated by Chile's national railway, Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado, connect Santiago to Temuco, in the central-southern part of the country. All such trains arrive and depart from the Estación Central ("Central Station").
बसें
Bus companies provide passenger transportation from Santiago to most areas of the country, while some also provide parcel-shipping and delivery services.
राजपथ

Toll road, inter-urban free flow highways connect the city's extremes, including the Vespucio Highway (which surrounds the city describing a semi-circle), Autopista Central (which crosses the city in a North-South direction), and the Costanera Norte (which runs from the eastern edge, in Las Condes to the international airport and the higways to Valparaíso on the western side of the city).
मेट्रो
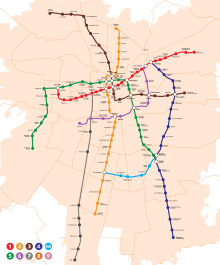
The Santiago Metro has five operating lines. Two subway lines (Line 4 and 4A) and an extension of Line 2 were inaugurated during late 2005 and 2006. The system is under expansion, and extensions are going to be built on Lines 1 and 5 throughout 2009.
परिवहन व्यवस्था

Transantiago is the name for the city's public transport system. It works by combining local (feeder) bus lines, main bus lines and the Metro network. It includes an integrated fare system, which allows passengers to make bus-to-bus or bus-to-metro transfers for the price of one ticket, using a single contactless smartcard.
Introduced on February 10 2007, it attempted to rationalize bus routes by eliminating redundancy, patent in the previous chaotic system run by thousands of independent bus operators. The plan backfired, however, as the decreased bus fleet and the newer routes proved insufficient to properly serve a population inadequately prepared for the changes. The major complaints are the lack of buses and their inconsistent frequencies, missing or poor infrastructure (such as segregated corridors, pre-paid areas and bus stops), the network's coverage, and the number of transfers needed for longer trips. As a result, users have overcrowded the Metro, which they see as fast and predictable.
टैक्सी
Taxicabs can usually be found on the streets and are painted black with yellow roofs; unmarked taxis may be called up by telephone (Radiotaxis). Colectivos are shared taxicabs that carry passengers along a specific route, for a fixed fee.
राजनैतिक डिविजन
Greater Santiago extends throughout 37 municipalities and covered 64,140 ha in 2002. The majority of Santiago lies within the same named province, with some peripheral areas contained in the provinces of Talagante, Maipo and Cordillera. Specifically, Santiago joins the cities of San Bernardo (Maipo province) and Puente Alto (Cordillera province) to form the Greater Santiago conurbation.
The province of Santiago is divided into 32 municipalities (comunas in Spanish). Each municipality in Chile is headed by a mayor (alcalde) elected by voters every four years. The members of the municipal council (concejales) are elected in the same election on a separate ballot.

सांस्कृतिक जीवन




संगीत
There are two symphonic orchestras:
- Orquesta Filarmónica de Santiago, which performs in the Teatro Municipal
- Orquesta Sinfónica de Chile, dependent of the Universidad de Chile, performs in its theater.
There are also various jazz establishments, the most notable being the Club de Jazz in Ñuñoa. The city has a very vibrant underground music scene. Some of its most popular venues are La Batuta in Ñuñoa and Blondie's disco in downtown Santiago.
संग्रहालय
Museums include:
- Centro Cultural Palacio de La Moneda, newest and biggest cultural space, beneath the Citizenry Square, in the south front of the government palace La Moneda
- Museo Arqueológico de Santiago
- Museo de Santiago Casa Colorada
- Museo Catedral Metropolitana
- Museo Colonial San Francisco
- Museo Chileno de Arte Precolombino
- Museo Histórico Nacional
- Museo Nacional de Bellas Artes
- Museo de Arte Contemporáneo
- Museo Interactivo Mirador
- Museo Artequín
- Museo de Ciencia y Tecnología
- Museo Ferroviario
- Museo de la Solidaridad "Salvador Allende"
- Palacio Cousiño
- La Chascona, Pablo Neruda's house, now a museum
मनोरंजन
The city's main parks are:
- San Cristóbal Hill (Cerro San Cristóbal), which includes the Santiago Metropolitan Park Zoo
- O'Higgins Park (Parque O'Higgins)
- Forestal Park (Parque Forestal), park located at the city centre alongside Mapocho river
- Cerro Santa Lucía
Modern ski resorts within an hour's drive east from the city include:
- Farellones
- Valle Nevado
- La Parva
- Portillo [1] is about three hours away.
Some of the country's most important winegrowing areas lie in the nearby Maipo and Aconcagua Valleys. Several vineyards are located in this area:
Cultural places to visit include:
- Museo de Bellas Artes
- Barrio Bellavista, cultural and bohemian neighborhood
- Central Station, railway station designed by Gustave Eiffel
- Víctor Jara Stadium
- Ex National Congress
- Plaza de Armas, downtown square
- Palacio de La Moneda, government palace
Main Sport Venues:
- Estadio Nacional (site of the 1962 World Cup final) 65.000 all-seated
- Estadio Monumental David Arellano 62.000 all-seated
- Estadio Santa Laura 28.500 all-seated
- Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo 20.000 all-seated
धर्म


Most of Chile's population is Catholic and Santiago is no exception. According to the National Census, carried out in 2002 by the National Statistics Bureau (INE), in the Santiago Metropolitan Region, 3,129,249 people 15 and older identified themselves as Catholics, equivalent to 68.7% of the total population, while 595,173 (13.1%) described themselves as Evangelical Protestants. Around 1.2% of the population declared themselves as being Jehovah's Witnesses, while 0.9% identified themselves as Latter-day Saints (Mormons), 0.25% as Jewish, 0.11% as Orthodox and 0.03% as Muslim. Approximately 10.4% of the population of the Metropolitan Region stated that they were atheist or agnostic, while 5.4% declared to follow other religions.[8]
संदर्भ
- ↑ Brief report of the fire (Spanish)
- ↑ Revista Ecoamérica. "Cruzada ambiental por el Mapocho limpio" (Spanish में). अभिगमन तिथि 2008-02-11.
permitirá pasar del 68 al 81% en el tratamiento de las aguas servidas
|author-link1=के मान की जाँच करें (मदद)सीएस1 रखरखाव: नामालूम भाषा (link) - ↑ El Mercurio. "Región Metropolitana saneará el 100% de aguas servidas al 2010" (Spanish में). Fundación Terram. अभिगमन तिथि 2008-02-11.सीएस1 रखरखाव: नामालूम भाषा (link)
- ↑ Comisión Regional Metropolitana del Medio Ambiente. "Agua, Recurso Escaso y Vital" (Spanish में). अभिगमन तिथि 2008-11-02.
se calcula que sólo el 77% de las industrias del país cumple con la norma de RILES existente
|author-link1=के मान की जाँच करें (मदद)सीएस1 रखरखाव: नामालूम भाषा (link) - ↑ "Mapocho urbano limpio: El río soñado" (PDF). अभिगमन तिथि 2008-11-02.
Proyecto Mapocho Urbano Limpio
- ↑ Fundación Futuro. "Proyecto Mapocho" (Spanish में).सीएस1 रखरखाव: नामालूम भाषा (link)
- ↑ Comisión Regional Metropolitana del Medio Ambiente. "Ruidos molestos en Santiago" (Spanish में). अभिगमन तिथि 2008-02-11.
cerca de un 70% de la población santiaguina está expuesta a serias interferencias de su sueño por ruido que excede 65 dB
|author-link1=के मान की जाँच करें (मदद)सीएस1 रखरखाव: नामालूम भाषा (link) - ↑ INE, Chile, 2002 Census

